|
Combined experimental and computational study of CO oxidation promoted by Nb in manganese oxide octahedral molecular sieves |
|
|
|
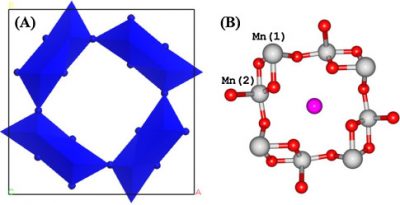
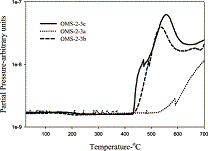
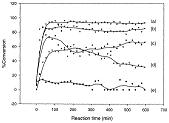
Framework-substituted Mn oxide octahedral molecular sieves with different Nb concentrations (2–20 mol% Nb-K-OMS-2) were synthesized via a single-step reflux method allowing for direct incorporation of the dopant into the mixed-valent Mn structure. Their specific surface areas ranged from 75 to 199 m2 g−1 with modified composition, size, morphology, porosity, thermal stability, and redox properties depending on the extent of substitution. Catalytic testing showed that the Nb-K-OMS-2 materials were active for CO oxidation and that the presence of Nb significantly enhanced the activity of pure K-OMS-2. For example, the conversions of 1% CO at 100 °C using 0%, 2%, 5%, 10%, 15%, and 20% Nb-K-OMS-2 were 4%, 10%, 25%, 62%, 59%, and 41%, respectively. When the O2 concentrations increased from 1% to 10% at 120 °C, the activities of 10% and 15% Nb-K-OMS-2 materials were improved by as much as 61% and 69%, respectively. These catalysts were also stable and less prone to deactivation by moisture (∼3% H2O) at temperatures >100 °C than pure K-OMS-2. Theoretical calculations revealed that the substitution of Mn by Nb was a thermodynamically-favorable process and produced electrophilic centers, which can provide favorable sites for strong CO adsorption on the Nb-K-OMS-2 surface. The interaction of CO at these sites exhibited the beneficial effect of Nb substitution in the K-OMS-2 materials. |
|
[Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2015, 163, 361-369] |
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
|
|
Potassium modified layered Ln2O2CO3 (Ln: La, Nd, Sm, Eu) materials: efficient and stable heterogeneous catalysts for biofuel production |
|
|
|
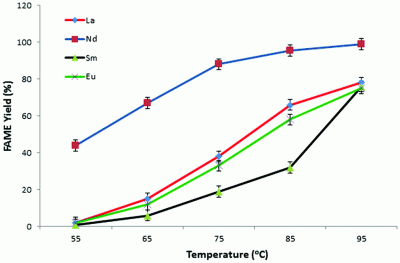
Potassium modified layered Ln2O2CO3 (Ln: La, Nd, Sm, Eu) biodiesel catalysts were prepared by a coprecipitation method followed by an overnight reflux. A high fatty acid methyl ester (FAME) yield (>95%) was achieved under mild reaction conditions (<100 °C). The FAME yields were investigated as a function of temperature and catalyst weight percentage. Nd2O2CO3 shows a better catalytic performance with a higher reaction rate than the industrial homogeneous KOH catalyst using both microwave irradiation and conventional heating methods. Approximately 100% FAME yield can be reached at 95 °C (microwave radiation) by 1.0 wt% Nd2O2CO3 within 10 min, while the same yield can be reached by 3.0 wt% Nd2O2CO3 at 95 °C (conventional heating method). In addition, leaching tests of the catalysts were performed; no leached rare earth metal ions were detected and the amounts of leached potassium were all under 5 ppm (ASTM standard). The synthesized layered Ln2O2CO3 materials offer a group of ideal alternative catalysts for industrial biodiesel production. |
|
[Green Chemistry, 2015, 17, 3600-3608] |
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
|
|
Facile Synthesis of Co3O4 @CNT with High Catalytic Activity for CO Oxidation under Moisture-Rich Conditions |
|
|
|
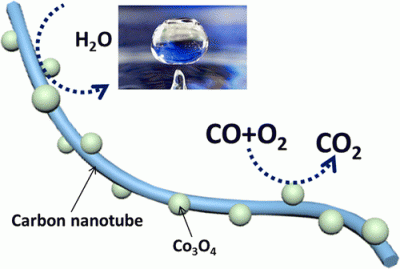
The catalytic oxidation reaction of CO has recently attracted much attention because of its potential applications in the treatment of air pollutants. The development of inexpensive transition metal oxide catalysts that exhibit high catalytic activities for CO oxidation is in high demand. However, these metal oxide catalysts are susceptible to moisture, as they can be quickly deactivated in the presence of trace amounts of moisture. This article reports a facile synthesis of highly active Co3O4@CNT catalysts for CO oxidation under moisture-rich conditions. Our synthetic routes are based on the in situ growth of ultrafine Co3O4nanoparticles (NPs) (∼2.5 nm) on pristine multiwalled CNTs in the presence of polymer surfactant. Using a 1% CO and 2% O2 balanced in N2 (normal) feed gas (3–10 ppm moisture), a 100% CO conversion with Co3O4@CNT catalysts was achieved at various temperatures ranging from 25 to 200 °C at a low O2 concentration. The modulation of surface hydrophobicity of CNT substrates, other than direct surface modification on the Co3O4catalytic centers, is an efficient method to enhance the moisture resistance of metal oxide catalysts for CO oxidation. After introducing fluorinated alkyl chains on CNT surfaces, the superhydrophobic Co3O4@CNT exhibited outstanding activity and durability at 150 °C in the presence of moisture-saturated feed gas. These materials may ultimately present new opportunities to improve the moisture resistance of metal oxide catalysts for CO oxidation. |
|
[Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2014, 6 (14), pp 11311-11317] |
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
|
|
Heterogeneous acidic TiO2 nanoparticles for efficient conversion of biomass derived carbohydrates |
|
|
|
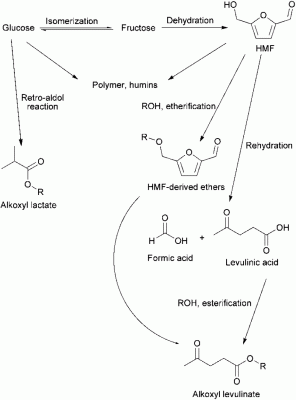
Selective conversion of biomass derived carbohydrates into fine chemicals is of great significance for the replacement of petroleum feedstocks and the reduction of environmental impacts. Levulinic acid, 5-hydroxymethyl furfural (HMF) and their derivatives are recognized as important precursor candidates in a variety of different areas. In this study, the synthesis, characterization, and catalytic activity of acidic TiO2 nanoparticles in the conversion of biomass derived carbohydrates were explored. This catalyst was found to be highly effective for selective conversion to value-added products. The nanoparticles exhibited superior activity and selectivity towards methyl levulinate from fructose in comparison to current commercial catalysts. The conversion of fructose to methyl levulinate was achieved with 80% yield and high selectivity (up to 80%). Additionally, conversions of disaccharides and polysaccharides were studied. Further, the production of versatile valuable products such as levulinic esters, HMF, and HMF-derived ethers was demonstrated using the TiO2 nano-sized catalysts in different solvent systems. |
|
[Green Chem, 2014, 16, 785-791] |
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
|
|
Direct Sonochemical Synthesis of Manganese Octahedral Molecular Sieve (OMS-2) Nanomaterials Using Cosolvent Systems, Their Characterization, and Catalytic Applications |
|
|
|
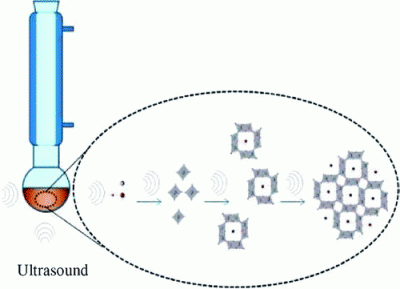
A rapid, direct sonochemical method has successfully been developed to synthesize cryptomelane-type manganese octahedral molecular sieve (OMS-2) materials. Very high surface area of 288 ± 1 m2/g and small particle sizes in the range of 1–7 nm were produced under nonthermal conditions. No further processing such as calcination was needed to obtain the pure cryptomelane phase. A cosolvent system was utilized to reduce the reaction time and to obtain higher surface areas. Reaction time was reduced by 50% using water/acetone mixed phase solvent systems. The cryptomelane phase was obtained with 5% acetone after 2 h of sonication at ambient temperature. Reaction time, temperature, and acetone concentration were identified as the most important parameters in the formation of the pure cryptomelane phase. OMS materials synthesized using the above-mentioned method were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), nitrogen sorption, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and Fourier transformation infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). OMS-2 materials synthesized using sonochemical methods (K-OMS-2SC) possess greater amounts of defects and hence show excellent catalytic performances for oxidation of benzyl alcohol as compared to OMS-2 synthesized using reflux methods (K-OMS-2REF) and commercial MnO2. |
|
[Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 705-712] |
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
|
|
Hydrophobic Polymer-Coated Metal Oxide Catalysts for Effective Low-Temperature Oxidation of CO under Moisture-Rich Conditions |
|
|
|
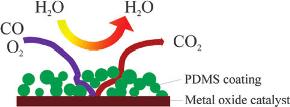
For the past several decades, the oxidation of carbon monoxide (CO) has become important in numerous applications, such as air/gas purification, life-support respirators, exhaust pollution reduction for automobiles/factories and Pt electrode protection in the low-temperature fuel cell system. This results in a pressing need for CO oxidation catalysis; and many catalyst systems (noble metals, metal oxides, and composites) have been studied for high CO conversion at various temperatures and environments. Among them, metal oxide catalysts with low production costs and high CO oxidation activity proved to be the most attractive. Most CO oxidation applications involve moist environments with rapid flow rates, so highly moisture tolerant catalysts are necessary. Here, we demonstrate the first example of the preparation and evaluation of a highly water-tolerant, hydrophobic polymer coated metal oxide catalyst for CO oxidation. |
|
[ Chem. Mater.(2010), XXX, 000–000 A, early view] |
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
|
|
|
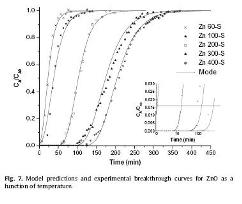
A com. available zinc oxide with a bimodal micro- and mesopore size distribution was investigated as a desulfurizing sorbent in a fixed- bed reactor at low temps. from 60 to 400 °C. Fresh and sulfided materials were characterized by X- ray diffraction (XRD) , BET sp. surface area, pore vol., SEM /EDX, TGA /DSC and in situ X- ray diffraction (XRD) . The sorbent’s sorption capacity at breakthrough increased with the sulfidation temp. reaching 87 % of the theor. value for desulfurization at 400 °C. A deactivation model that considers the activity of the solid reactant was used to fit the exptl. data. Good agreement between the exptl. breakthrough curves and the model predictions was obtained. |
|
[ Microporous and Mesoporous Materials (2010), 127(3), 190-197 ] |
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
|
|
Manganese dioxide as a new cathode catalyst in microbial fuel cells |
|
|
|
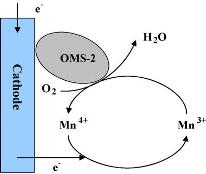
This study focused on manganese oxides with a cryptomelane- type octahedral mol. sieve (OMS- 2) structure to replace platinum as a cathode catalyst in microbial fuel cells (MFCs) . Undoped (ud- OSM- 2) and three catalysts doped with cobalt (Co- OMS- 2) , copper (Cu- OMS- 2) , and cerium (Ce- OMS- 2) to enhance their catalytic performances were investigated. The novel OMS- 2 cathodes were examd. in granular activated carbon MFC (GACMFC) with sodium acetate as the anode reagent and oxygen in air as the cathode reagent. The results showed that after 400 h of operation, the Co- OMS- 2 and Cu- OMS- 2 exhibited good catalytic performance in an oxygen redn. reaction (ORR) . The voltage of the Co- OMS- 2 GACMFC was 217 mV, and the power d. was 180 mW m- 2. The voltage of the Cu- OMS- 2 GACMFC was 214 mV and the power d. was 165 mW m- 2. The internal resistance (R in) of the OMS- 2 GACMFCs (18 ± 1 O) was similar to that of the platinum GACMFCs (17 O) . Furthermore, the degrdn. rates of org. substrates in the OMS- 2 GACMFCs were twice those in the platinum GACMFCs, which enhance their wastewater treatment efficiencies. This study indicated that using OMS- 2 manganese oxides to replace platinum as a cathodic catalyst enhances power generation, increases contaminant removal, and substantially reduces the cost of MFCs. |
|
[ Journal of Power Sources (2010), 195(9), 2586-2591 ] |
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
|
| Methods and app. for activation of a low reactivity, non- polar chem. compd. to a catalyst is presented. At least one of (a) an oxidizing agent or a reducing agent and (b) a polar compd. is provided to the catalyst and the chem. compd. An a.c. is applied to the catalyst to produce an activation reaction in the chem. compd. This activation reaction produces a useful product. | |
|
[ U.S. Pat. Appl. Publ. (2009), US 2009134037 A1 20090528 ] |
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
|
|
g-MnO2 octahedral molecular sieve: Preparation, characterization, and catalytic activity in the atmospheric oxidation of toluene |
|
|
|
A synthesized g-MnO2 octahedral molecular sieve was characterized and used to catalyze solvent-free atmospheric oxidation of toluene with molecular oxygen. The g-MnO2 showed excellent catalytic activity and good selectivity under the mild atmospheric reflux system at a low temperature (110 ◦C). Under optimized conditions, a 47.8% conversion of toluene, along with 57% selectivity of benzoic acid and 15% of benzaldehyde were obtained. The effects of reaction time, amount of catalyst and initiator, and the reusability of the catalyst were investigated. |
|
[ Appl. Catal., A (2009) 355, (1-2), 169-175 ] |
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
|
|
Cyclohexane oxidation catalyzed by manganese oxide octahedral molecular sieves-Effect of acidity of the catalyst |
|
|
|
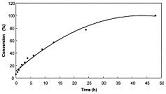
Oxidation of cyclohexane is an important industrial process, its oxidation products, cyclohexanol and cyclohexanone are raw materials for adipic acid and caprolactam synthesis. Acid exchanged cryptomelane type manganese oxide octahedral molecular sieves (H-K-OMS-2) was used for liquid phase oxidation of cyclohexane with t-butyl hydroperoxide as an oxidant. The H+ form of K-OMS-2 was synthesized by ion-exchange of K-OMS-2 with concentrated nitric acid. H-K-OMS-2 has been found to be an efficient catalyst for the oxidation of cyclohexane with a high conversion (∼60%). More than 90% selectivity for cyclohexanol and cyclohexanone was obtained. A turn over number (TON) of 73 was obtained in 24 h at 80 ◦C and if we consider only contributions of acidic manganese sites then the TON is 287. Effect of increase in number of acid sites of the K-OMS-2 was correlated with the increase in conversion. The reactions were carried out in a semi-batch reactor at 80 ◦C using acetonitrile as solvent. Effects of solvent, temperature, and amount of t-butyl hydroperoxide on conversion and selectivity were studied. |
|
[ J. Catal. (2009) 262, (2), 304-313 ] |
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
|
|
Manganese octahedral molecular sieve catalysts for selective styrene oxide ring opening |
|
|
|
Manganese octahedral molecular sieve (OMS) catalysts prepared by different methods have been employed for terminal ring opening of epoxides. Conversions ranging from 14% to 80% were obtained depending on the properties of the OMS catalysts. The catalysts act as Lewis acids in the reaction to facilitate nucleophilic attack on styrene oxide. Doping with other transition metals such as V, W, and Mo may alter the Lewis acidity of the materials and hence, leads to significant enhancement in conversions (100%) and selectivities for the ring opening. Effects of different solvents and nucleophiles were also studied in the reaction. This process usingOMS catalysts is environmentally friendly and the catalysts can be reused without loss of activity. |
|
[ Catal. Today (2009) 140, (3-4), 162-168 ] |
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
|
|
Green Decomposition of Organic Dyes Using Octahedral Molecular Sieve Manganese Oxide Catalysts |
|
|
|
The catalytic degradation of organic dye (methylene blue, MB) has been studied using green oxidation methods (tertiary-butyl hydrogen peroxide, TBHP, as the oxidant with several doped mixed-valent and regular manganese oxide catalysts in water) at room and higher temperatures. These catalysts belong to a class of porous manganese oxides known as octahedral molecular sieves (OMS). The most active catalysts were those of Mo6+- and V5+-doped OMS. Rates of reaction were found to be first-order with respect to the dye. TBHP has been found to enhance the MB decomposition, whereas H2O2 does not. Reactions were studied at pH 3-11. The optimum pH for these reactions was pH 3. Dye-decomposing activity was proportional to the amount of catalyst used, and a significant increase in catalytic activity was observed with increasing temperature. XRD, EDX, and TGA studies showed that no changes in the catalyst structure occurred after the dye-degradation reaction. The products as analyzed by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) showed that MB was successively decomposed through different intermediate species. |
|
[ J. Phys. Chem. A (2009) 113, (8), 1523-1530 ] |
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
|
|
Manganese octahedral molecular sieves catalyzed tandem process for synthesis of quinoxalines |
|
|
|
An efficient environmentally benign tandem synthetic route to prepare quinoxalines leading to 100% yields using reusable manganese oxide octahedral molecular sieves (OMS-2) is described.
|
|
[ Green Chemistry ( 2008 ), 10(10), 1029-1032 ] |
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
|
|
Kinetics and Mechanism of 9H-Fluorene Oxidation Catalyzed by Manganese Oxide Octahedral Molecular Sieves |
|
|
|
Sift fluorene into a bowl : Manganese oxide octahedral molecular sieves (OMS-2), with the overall composition KMn8O16n.H2O, catalyze the mild, green, and efficient oxidation of 9H-fluorene to 9-fluorenone. The involvement of lattice oxygen species has been implicated in a free-radical chain mechanism. In terms of reaction kinetics, the breaking of the C-H bond is rate controlling.
|
|
[ChemSusChem (2008), 1(3), 182 – 185] |
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
|
|
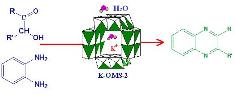
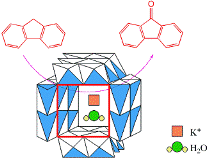
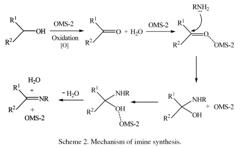
Tandem catalysis: Direct catalytic synthesis of imines from alcohols using manganese octahedral molecular sieves |
|
|
|
Tandem processes involving catalysts can offer unique and powerful strategies for converting simple starting materials into more complex products in a single reaction vessel. Imines were synthesized directly from alcohols via a tandem catalytic process using manganese octahedral molecular sieves (OMS-2) as catalyst. The synthesis proceeds through two steps: an oxidation of the alcohols to carbonyls followed by the nucleophilic attack by an amine on the carbonyl to form the imine. OMS-2 acts as a bifunctional catalyst and catalyzes two mechanistically distinct processes in a single reaction vessel under the same conditions. Conversions up to 100% were obtained for benzylic alcohols with this efficient, environmentally friendly catalytic reaction. The advantages of this process are that the intermediates need not be isolated and the catalysts can be reused upon simple filtration without loss of activity. |
|
[Journal of Catalysis 2008, 253, 269–277] |
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
|
|
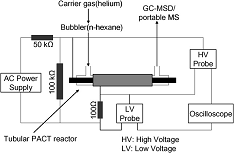
Generation of hydrogen and light hydrocarbons for automotive exhaust gas purification: Conversion of n-hexane in a PACT reactor |
|
|
|
Conversion of n -hexane, used as a model hydrocarbon, was carried out over iron and nickel electrodes in an alternating current (AC) discharge plasma and catalysis integrated technologies (PACT) reactor to instantly produce hydrogen and light alkanes and alkenes, at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. The possible application for this technology could be in automotive exhaust gas purification. Catalytic effects of metal electrodes are involved in the reactions, with iron electrodes showing obviously higher catalytic activity on addition reactions compared with nickel electrodes. Cracking of carbon�carbon bonds is the dominant reaction. Catalytic dehydrogenation of hexane is the source of hydrogen.
|
|
[Journal of Catalysis, 2007 , 250(1), 67-74] |
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
|
|
Preparing irradiated catalysts and the catalysts made for oxidation of hydrocarbons |
|
|
Processes for preparing mixed metal oxide catalysts suitable for partial oxidation of alkanes, alkenes and mixtures thereof, where in the processes comprise the steps of: providing an aqueous aerosol of one or more metal oxide catalyst precursors; and irradiating the aqueous aerosol of one or more metal oxide catalyst precursors with microwave energy. Optionally, the catalyst may be further modified using one or more chemical treatments, one or more physical treatments and one or more combinations of chemical and physical treatments, to further improve catalyst performance characteristics. |
|
|
[U.S. Pat. Appl. Publ. 2007, US, 10pp.] |
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
|
|
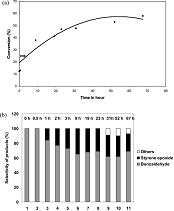
Role of Manganese Oxide Octahedral Molecular Sieves in Styrene Epoxidation |
|
|
|
Manganese oxide octahedral molecular sieves having 2×2 tunnel structure (OMS-2) and synthesized by different methods were used for studying styrene oxidation with tert -butyl hydroperoxide (TBHP) as the oxidant. The catalytic activity of the as-synthesized OMS-2 materials was investigated. The physical and chemical properties of the OMS-2 materials are related to their activity in styrene oxidation. This particular study emphasizes the acid-base properties and the porous nature of these materials, and their role in styrene oxidation. Results of styrene oxidation reveal that acidity coupled with high porosity play a crucial role in these catalytic reactions. A desired acidity coupled with pore volume found in OMS-2 synthesized by reflux ethods (OMS-2R) and high-temperature methods (OMS-2HT) produces materials with higher styrene conversion and styrene oxide selectivity when compared with OMS-2 synthesized by solvent free (OMS-2S), microwave (OMS-2MW), or hydrothermal methods (OMS-2HY). Transition metal doped OMS-2 catalysts show better selectivity of styrene oxide when compared to their undoped catalysts. |
|
[Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2006, 110(14), 7592-7599] |
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
|
|
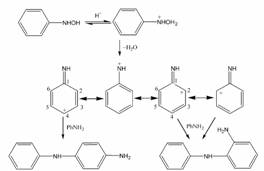
Manganese oxide octahedral molecular sieve catalysts for synthesis of 2-aminodiphenylamine |
|
|
|
Cryptomelane-type manganese oxides octahedral molecular sieve (K-OMS-2) were used for the acid-catalyzed condensation of phenylhydroxylamine with aniline to produce 2-aminodiphenylamine. The H+-exchanged K-OMS-2 was found to be an efficient catalyst for this reaction. The reaction showed high selectivity (~96%) for the ortho isomer of aminodiphenylamine compared with the para product. The effect of the amount of H+ exchange and temperature was investigated. |
|
[Journal of Catalysis, 2005, 236(2), 387-391] |
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
|
|
Effect of a Metal Alloy Fuel Catalyst on Bacterial Growth |
|
|
|
Manymicroorganisms have been demonstrated to utilize petroleum fuel products to fulfill their nutritional requirement for carbon. As a result, the ability of these microbes to degrade fuel has both a deleterious affect as well as beneficial applications. This study focused on the undesired ability of bacteria to grow on fuel and the potential for some metal alloys to inhibit this biodegradation. The objective of this study was to review the pattern of growth of two reference strains of petroleum-degrading bacteria,Pseudomonas oleovorans and Rhodococcus rhodocrous , in a specific hydrocarbon environment in the presence of a commercially available alloy. The alloy formulated and supplied by Advanced Power Systems International Inc. (APSI) is sold for fuel reformulation and other purposes. The components of the alloy used in the study were antimony, tin, lead, and mercury formulated as pellets. Surface characterization also showed the presence of tin oxide and lead amalgam phases. Hydrocarbon used for the study was primarily 87-octane gasoline. The growth of the bacteria in the water and mineral-supplemented gasoline mixture over 6-8 weeks was monitored by the viable plate count method. While an initial increase in bacteria occurred in the first week, overall bacterial growth was found to be suppressed in the presence of the alloy. Results also indicate that the alloy surface characteristics that convey the catalytic activity may also contribute to the observed antibacterial activity.
|
|
[Langmuir, 2005, 21, 10655-10661] |
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
|
|
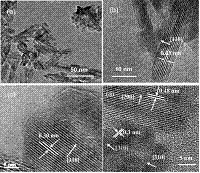
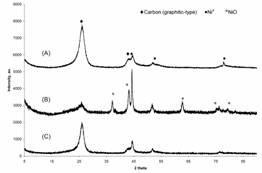
Synthesis and Catalytic Activity of Cryptomelane-Type Manganese Dioxide Nanomaterials Produced by a Novel Solvent-Free Method |
|
|
|
Cryptomelane-type K-OMS-2 nanomaterials with high surface area (156 m2/g) have been synthesized via a low-temperature solvent-free method in a very short time (1 h). Field emission scanning electron microscopy and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy images reveal that these materials have nanorod morphologies with average diameters of about 10 nm and lengths of about 50 nm. These are different from the long fiberous morphologies of OMS-2 materials made by conventional reflux or hydrothermal methods. X-ray diffraction and Brunauer-Emmett-Teller studies indicate that these materials have small crystallite sizes (9.8 nm) and that they are mesoporous with a uniform pore size distribution centered at 12 nm. These K-OMS-2 materials show improved catalytic activity for the oxidation of alcohols compared with the conventional K-OMS-2 materials, which may be due to their higher surface areas and novel surface properties. This fast, inexpensive, and environmentally friendly solvent-free method has he potential of being used in scaled-up syntheses of K-OMS-2 and other transition-metal-ion-substituted manganese oxide nanomaterials.
|
|
[Chemistry of Materials, 2005, 17(21), 5382-5389] |
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
|
|
Decomposition of methane with an autocatalytically reduced nickel catalyst |
|
|
|
Thermal decomposition of nickel acetate ( T > 300 ° C) dispersed on either silica or cordierite supports resulted in a mixture of Ni0/NiO that was catalytically active for the decomposition of methane to produce CO-free hydrogen, without the need for any pretreatment (i.e., using H 2 at high temperature (> 500 °C) for at least 2 h). The carbon yield (gC/gNi) for the catalysts supported on SiO2 (200�300 m2/g) increased with an increase in the catalyst NiO mean crystallite size. XRD and FE-SEM studies confirmed the formation of graphitic-type carbon filaments during the methane decomposition.
|
|
[Journal of Catalysis, 2005, 233, 317�326] |
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
|
|
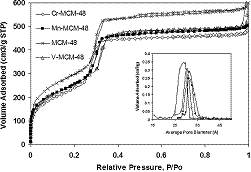
Synthesis and characterization of TM-MCM-48 (TM = Mn, V, Cr) and their catalytic activity in the oxidation of styrene |
|
|
|
Transition-metal (TM) species (Mn, V, and Cr) were incorporated by an anion-exchange method into MCM-48. The TM-MCM-48 materials were characterized by XRD, HRTEM, N 2 adsorption�desorption, ESR, Raman, and NH3-TPD. The structural and textural properties of the materials are discussed, as is the nature of the TM species introduced in the mesoporous host. The catalytic activity and selectivity of the TM-MCM-48 in the oxidation of styrene with TBHP as an oxidant agent are explored. All of the catalysts produce benzaldehyde and styrene oxide as the main products. Mn-MCM-48 showed the highest selectivity for styrene oxide, but with a maximum conversion of 58%. V-MCM-48 shows the highest conversion of styrene (100%) and the highest selectivity (88%) for benzaldehyde. The Cr catalyst shows the poorest performance in terms of selectivity. The TM-MCM-48 catalysts are very active in the oxidation of styrene, and their activity depends on the nature of the transition metal used.
|
|
[Journal of Catalysis, 2005, 233(1), 60-67] |
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
|
|
Regioselective catalytic process for preparing ortho-substituted phenylamines |
|
|
Ortho-substituted phenylamines (e.g., 1,2-diaminobenzene) are prepared by contacting phenylhydroxylamine, optionally substituted with at least one inert substituent, with a nucleophilic reagent (e.g., aniline) in the presence of a manganese oxide catalyst at 10-170 °C and a pressure from subatmospheric to superatmospheric. |
|
|
[U.S. Pat. Appl. Publ., 2004, US 20041624444, 7 pp.] |
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
|
|
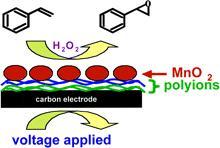
Electrochemical Catalysis of Styrene Epoxidation with MnO2 Nanoparticles and H2O2
|
|
|
|
Films of polyions and octahedral layered Mn oxide (OL-1) nanoparticles on C electrodes made by layer-by-layer alternate electrostatic adsorption were active for electrochemical catalysis of styrene epoxidation in solution in the presence of H2O2 and oxygen. The highest catalytic turnover was obtained by using applied voltage -0.6 V vs.SCE, O2, and 100 mM H2O2. 18O isotope labeling experiments suggested oxygen incorporation from 3 different sources: mol. oxygen, H2O2, and/or lattice oxygen from OL-1 depending on the potential applied and the oxygen and H2O2concentrations. Oxygen and H2O2 activate the OL-1 catalyst for the epoxidation. The pathway for styrene epoxidation in the highest yields required oxygen, H2O2, and a reducing voltage and may involve an activated oxygen species in the OL-1 matrix.
|
|
[Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2004, 126, 7676-7682] |
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
|
|
Liquid-phase epoxidation of olefins by manganese oxide octahedral molecular sieves
|
|
|
|
Manganese oxide octahedral molecular sieves with a cryptomelane structure (OMS-2) were used to catalyze the oxidation of cyclic olefins and benzylic double bonds with tertiary-butyl hydroperoxide (TBHP) as the oxidant. OMS-2 showed good catalytic activity with high selectivity under mild conditions (substrate:oxidant molar ratio of 1:1) for the oxidation of different substrates that were studied. Cyclooctene gets oxidized to cyclooctene epoxide selectively in the presence of OMS-2 among the different substrates used for oxidation. The order of reaction with respect to cyclooctene was determined to be pseudo-first order using OMS-2 and excess TBHP. The effects of time, reaction temperature, solvents, and amount of catalyst were investigated. Various reaction conditions and conversion of cyclooctene were maximized at 60 °C using acetonitrile as the solvent. |
|
[Journal of Catalysis, 2004, 224, 288-296] |
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
|
|
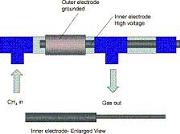
Metal effect and flow rate effect in the hydrogen production from methane
|
|
|
|
The metal effect of the inner electrode used for the decomposition of methane and the resulting evolution of hydrogen by discharge plasmas was investigated. Several different electrodes were used including noble metals such as palladium and other metals such as iron and copper. The noble metals showed the highest activity in methane decomposition and hydrogen production. Nickel and gold showed considerable deactivation, whereas the activity of iron decreased less. Coated electrodes with copper and tin oxide nanoparticles exhibited high activity in these reactions. The effect of the flow rate and the cleaning of the electrode were examined as further objectives of this study. The decomposition of methane and the evolution of hydrogen decreased with increasing flow rate in a neg. exponential manner due to the lower residence time. The cleaning of the electrode has a profound effect on the conversions and allows one to observe the catalytic effect of the metal electrodes, which are otherwise covered by coke produced in the reaction. A mechanism was developed using data obtained from mass spectrometry and combined gas chromatography and mass spectrometry. |
|
[Catalysis Today, 2004, 89, 35-45] |
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
|
|
Selective oxidation of alcohols using octahedral molecular sieves
|
|
|
|
Manganese oxides having a tunnel structure (OMS-2) have been utilized as selective catalysts for alcohol oxidation. In this study manganese oxide catalysts were synthesized in different media and modified by exchanging the tunnel cation by H+, using acid treatment or exchanging with NH4+ followed by thermolysis. Various alcohol oxidations were performed using these catalysts to ascertain the influence of synthesis method on their activity. A correlation is made between lattice oxygen instability and activity of the catalysts, which indicates involvement of the lattice oxygen in the mechanism. The exchange of the tunnel cation with the smaller H+ ions leads to weakening of the Mn-O bond, as verified by temperature programmed desorption (TPD) results. Only the chemisorbed oxygen on the surface (O-) and the lattice oxygen in the layers close to the surface is involved in the oxygen transfer during the reaction.
|
|
[Catalysis Today, 2003, 85, 225-233] |
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
|
|
Selective N,N-methylation of aniline over cocrystallized zeolites RHO and zeolite X (FAU) and over Linde type L (Sr,K-LTL)
|
|
|
|
Alkylation of aniline (PhNH2) with methanol (MeOH) over cocrystallized zeolite RHO-zeolite X (FAU) and over zeolite Linde type L (Sr,K-LTL) as catalysts has been studied. Cocrystallized zeolite RHO-zeolite X (FAU) favors the formation of N,N-dimethylaniline (NNDMA) with high selectivity >90%, having an advantage over pure zeolite X (FAU) of staying active even after 10 h of reaction. Activity of cocrystallized RHO-zeolite X (FAU) is higher than that for Sr,K-LTL in terms of the production of N,N-dimethylaniline.
|
|
[Journal of Catalysis, 2003, 217, 107-116] |
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
|
|
A selective process to prepare triacetone amine
|
|
|
2,2,6,6-Tetramethyl-4-oxopiperidine (TAA) is an intermediate for polymer light stabilizer, for drugs, and for nitroxyl radicals of piperidine and pyrolidone derivs. Numerous methods have been reported for the synthesis of TAA. Perhaps the widest scope of any patent pertaining to the synthesis of TAA was issued to Ciba Geigy, which claims the broad use of any acid in the condensation of4 mol of acetone with 1 mol of ammonia ³. Another route to triacetone amine that involves the conversion of acetone and ammonia to acetonine [5](2,2,4,4,6-pentamethyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyrimidine) is made from acetone, ammonia and a catalyst at room temp. After purification, acetonine is mixed with more than six equiv. of acetone and refluxed, yielding TAA in the presence of Lewis acids such as calcium, zinc, ammonium chloride, aluminum, or boron trifluoride. TAA can also be obtained from phorone, diacetone alc., diacetone amine instead of the condensation of acetone and ammonia or the condensation of acetonine and ammonia, but not economically. Included among the catalysts for the condensation of acetone with ammonia are several using calcium chloride as a catalyst leading to acetonine and TAA. An efficient, environmentally friendly, simple and economical route to TAA was reported. |
|
|
[Chemical Industries (Dekker), 2003, 89 (Catalysis of Organic Reactions), 559-564] |
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
|
|
Catalytic oxidation of alcohols using manganese oxides
|
|
|
A method of oxidizing an organic alcohol wherein the organic alcohol is contacted with a stoichiometric excess of oxygen in the presence of an effective catalytic amt. of a manganese-containing octahedral molecular sieve or octahedral layer. Primary alcohols are selectively oxidized to aldehydes, and secondary alcohols are selectively oxidized to ketones. |
|
|
[U.S. Pat. Appl. Publ., 2002, US 2002128506, 10 pp.] |
|